Orthotics for Chronic Lower Back Pain
Custom Orthotics | orthoticsnearme.com
Studies show that foot orthotics can play a role in alleviating and preventing the lower back pain. Foot orthotics can help manage low back pain by improving and stabilizing the position of the feet, which in turn improves every aspect of a person’s gait. This is thought to occur through improved impact absorption or attempting to improve the alignment of the leg though compensation for misalignment.
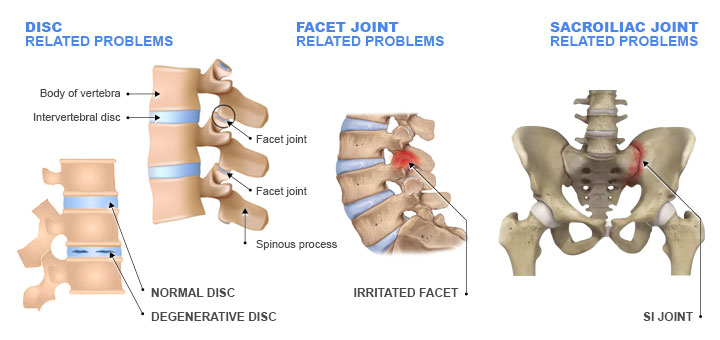
Causes of Lower Back Pain
Chronic lower back pain, the opposite of acute lower back pain is anything that lasts for longer than 3 months. The lower back pain syndrome is often described by patients as a dull, aching feeling that have varying degrees of severity. There are several medical conditions that account for approximately 80% of chronic lower back pain syndrome cases, including:
- Conditions related to intervertebral discs problems. The discs are jelly like donuts between vertebral bodies, the specialized bones that make up the spinal column. Each disk is about an inch in diameter and one-quarter inch thick. Degenerative disc disease or trauma may lead to inflammation which causes the lower back pain. This definition does not include patients with herniated disc.
- Facet joint related problems. Facet joints prevent excessive motion, over-twisting, or toppling over, the segments of the spine. Facet joints can become inflamed or traumatized, causing the lower back pain.
- Sacroiliac joint pain (SI joint pain). The causes for sacroiliac joint pain can be broken down into two categories, hyper-mobility which means there is excess motion in the joints, or hypo-mobility which means there is limited motion in the joints. Hypermobility can be caused by different reasons such as obesity, personal injury, previous surgery, aging, intensive sports or labor, pregnancy, etc. Hypomobility can also be caused by degenerative joint conditions such as arthritis.
- Conditions related to abnormal foot mechanics may also contribute to development of chronic low back pain syndrome. The foot is made up of a complex interaction of bones, ligaments, and muscles. These structures help the foot alternate between being a mobile, flexible adaptor and a stable, rigid lever. Basically, the foot functions in three primary ways:
- It provides a stable platform of support
- It attenuates impact upon loading
- It assists in efficient forward propulsion of the body
When we walk there is a load placed on the foot and the leg. The foot has varying ability to accept weight before injury results. In people with flat feet (over-pronated feet and ankles), the lower leg rotates inward. Flat feet are generally excessively mobile and the foot has a tendency to move too much. In this case, the ligaments and muscle associated with this area tend to be stressed more than normal, which can put stress on the knee, on the hip and on the back. This phenomenon is known as ‘kinetic chain’. Pronated feet and ankles cause the knees to turn inward which in turn shifts the angle where the thigh bone meets the pelvis, resulting in an unsteady hip posture that also destabilizes the spine. Overtime, walking and standing with the feet, legs, hips, and spine constantly out of alignment can cause overuse injuries contributing to back pain.
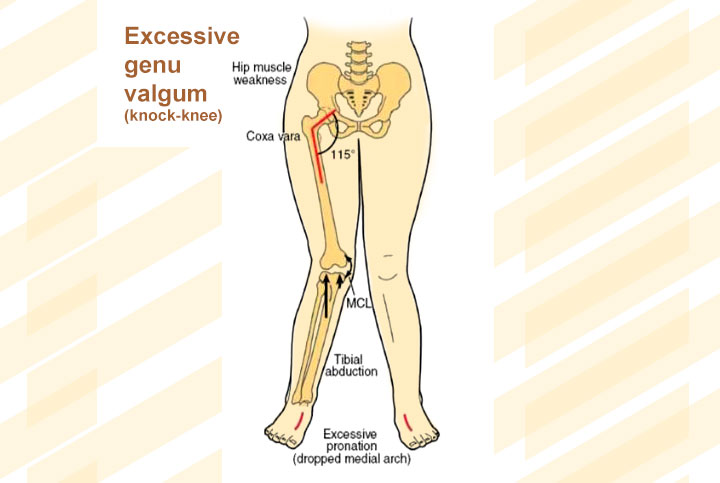
Pronated feet cause the knees to come together into a knocked-knee stance. Medical term is genu valgus. This also affects the angle of the hip, forcing the femur (thigh bone) to angle inward from the hip, which is medically known as coxa vara. The faulty angulation of the hips and knees then destabilizes the pelvis, which also affects overall posture and the spine.